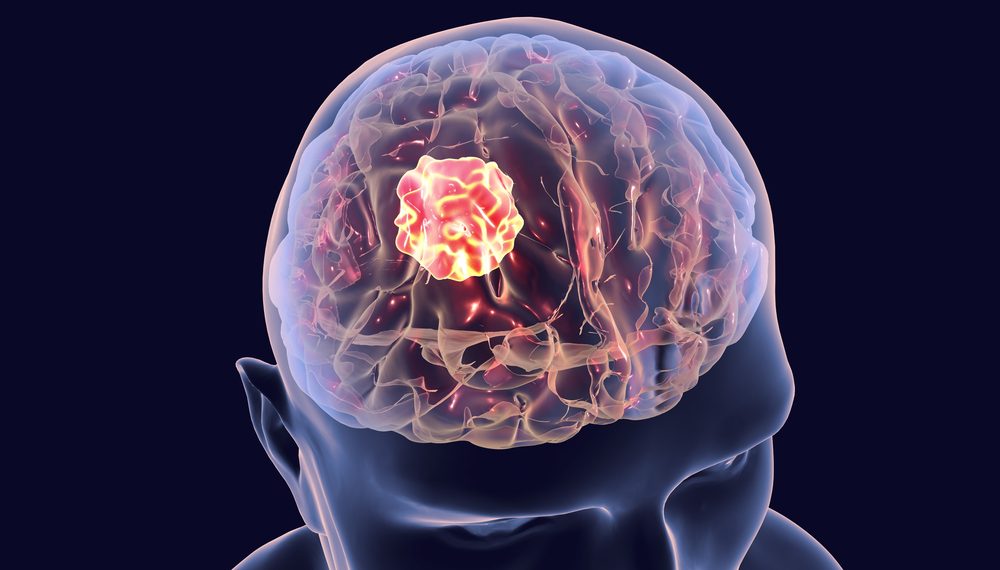
A stroke (a stream of consciousness disturbance) occurs when part of the central nervous system is damaged either because it is starved of blood or oxygen. The brain uses oxygen and glucose to obtain energy and perform functions such as movement, sensation, thought and language. If the supply of oxygen is reduced or cut off completely, brain cells begin to die, thus, a stroke is also called a cerebrovascular disorder, CVA, stroke or a brain attack. Since the symptoms of a stroke are exactly the same as those of a stroke, it is important that these conditions are treated right away.
The symptoms of a CVA and stroke are similar, however, there are a few major differences between the two medical emergencies. In a CVA, blood flow to the affected area is stopped or compromised and as a result, oxygen is not supplied to the brain. On the other hand, in a stroke, a direct blow to the head will temporarily cause a decrease in blood flow to the area but this normally develops after a short period of time, such as five to ten minutes.
Some of the symptoms of a CVA and stroke prevention include memory loss, seizures, headache, dizziness, flu-like symptoms, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing and pain in the muscles of the neck, face, arms and back. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should contact your doctor immediately. Early symptoms can save your life! Your doctor will perform an evaluation to discover the cause of your symptoms and recommend treatment. These steps of CVA and stroke prevention are discussed below.















Discussion about this post